seq command prints a sequence of numbers in Linux. It is super-fast in generating a list of sequential numbers.
The output of seq command can be piped to various other commands for additional functionality. The seq command is also useful in for loops and bash scripts.
This article will discuss different examples of the seq command to print a sequence of numbers in the Linux system.
Syntax for seq command
The general syntax to use the seq command is:
seq [OPTION] [FIRST] [INCREMENT] LAST
FIRST: the starting number in the sequence
LAST: the end number or limit in the sequence
INCREMENT: the increment number value in a sequence
1. Generate a sequence of numbers up to the specified number
When FIRST and INCREMENT are not given, the seq command uses the default value of 1 in both arguments.
If you provide only one argument to the seq command, it prints the sequence of numbers from 1 up to the specified number.
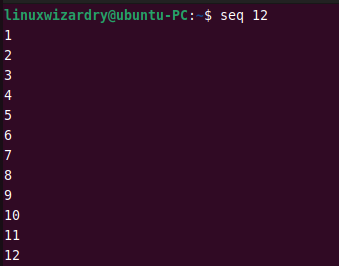
For example, this command generates a sequence of numbers from 1 to 12.
$ seq 12
Output:
2. Generate a sequence of numbers in a specific range
To print a sequence of numbers between two numbers, you have to specify both the FIRST and LAST arguments.
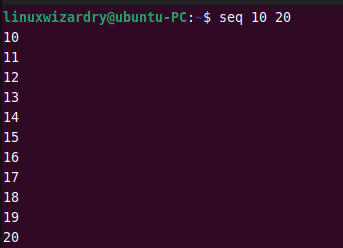
The following command generates a sequence of numbers from 10 to 20.
$ seq 10 20
Output:
3. Print sequence with different increment number
By default, the seq command uses the increment value of 1. To specify your own incremental number, use the following command.
seq FIRST INCREMENT LAST
The first number cannot be greater than the last number.
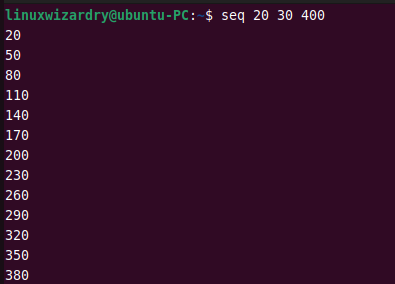
The following example prints the sequence of numbers from 20 to 200 with an increment of 30.
seq 20 30 400
Output:
4. Generate the sequence of decimal numbers
You can print the sequence of decimal numbers by using the start or increment value as a decimal number.
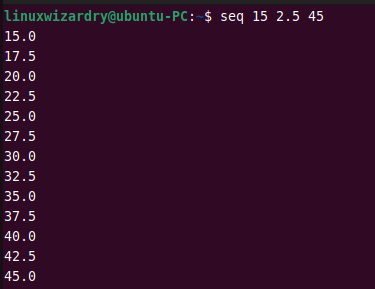
This command generates the sequence of floating point numbers from 15 to 45 with an increment of 2.5.
seq 15 2.5 45
Output:
5. Print the sequence of numbers backward
You can generate the sequence of numbers backward by specifying the negative increment value.
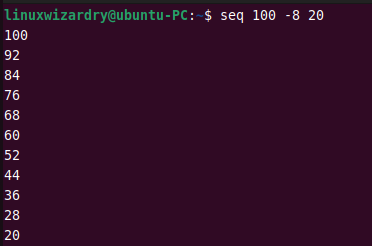
For example, the following command prints the sequence of numbers from 100 to 20 with an increment of -8.
seq 100 -8 20
Output:
6. Format the sequence of numbers in the same width
The -w is used to print all sequential numbers in the same width. It equalizes the width by adding leading zeroes to match the same width.
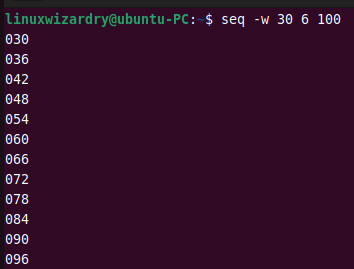
This command generates the sequence of numbers having the same width from 30 to 100 with an increment of 5.
seq -w 30 5 100
Output:
7. Print sequence of numbers with different separators
The seq command uses the newline character to separate the sequence numbers by default. That’s why each number is printed on a separate line.
The -s option tells seq command to use the specified character to separate the numbers.
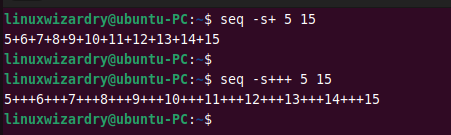
The following uses a plus sign + as the separator to print the sequence of numbers from 5 to 15.
seq -s+ 5 15
You can also specify multiple signs as separators.
seq -s+++ 5 15
Output:
8. Use C Format specifier to print sequence of numbers
The -f option allows you to use the C printf-style format to print the sequence of numbers. The %g is used for default numbers.
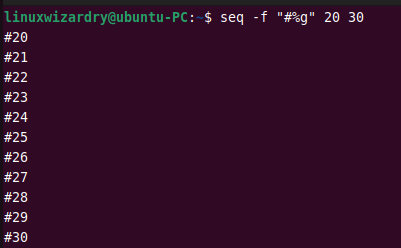
The following command prints the sequence of numbers from 20 to 30 with the padding of leading hash symbols #.
seq -f "#%g" 20 30
Output:
You can also format the string and insert the sequence of numbers in it.
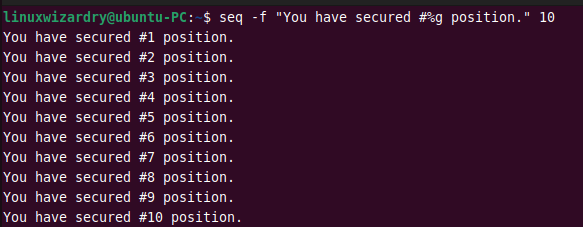
seq -f "You have secured #%g position." 10
Output:
9. Perform simple calculations with seq command
bc is a command-line calculator in Linux. You can pipe the output of the seq command to the bc command for doing some calculations like adding, subtracting, multiplying, etc.
You will need to separate the sequence of numbers using any of these mathematical symbols: +, -, *, and /.
The following command separates the sequence of numbers from 3 to 10 by a * symbol.
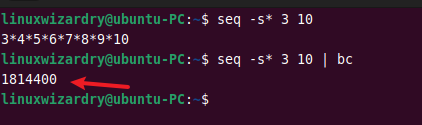
seq -s* 3 10
If the above command is piped to the bc command, it will multiply the numbers and print the result.
seq -s* 3 10 | bc
Output:
Similarly, you can perform addition and subtraction of numbers.
10. Write the sequence of numbers in a file
You can redirect and save the output of the seq command to a file using the > operator.
The following command generates the sequence of numbers starting from 40 and increments in 10 up to 200.
seq 40 10 200
To write the output in a test.txt file, you can run this command.
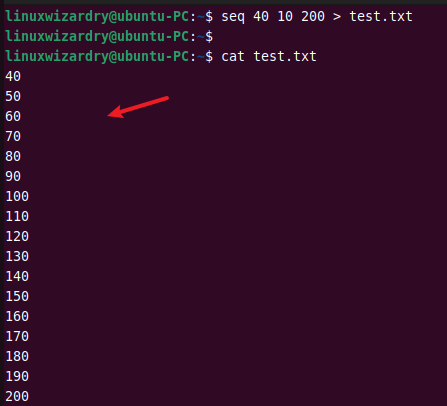
seq 40 10 200 > test.txt
Output:
11. Create Files Quickly with seq command
You can use seq command to create multiple files having the same name with different numbers very quickly.
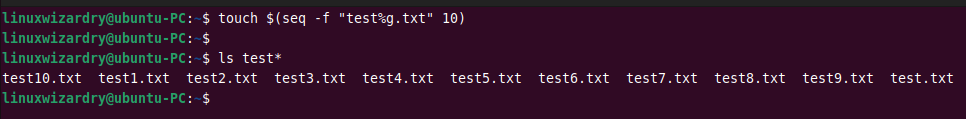
For instance, to create 10 files with names test1.txt, test2.txt, test3.txt, and so on, run the following seq command.
touch $(seq -f "test%g.txt" 10)
Output:
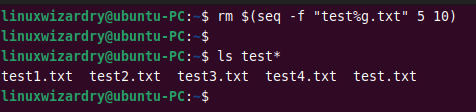
You can also remove such files using the seq command. The following command removes files from test5.txt up to test10.txt.
rm $(seq -f "test%g.txt" 5 10)
Output:
12. Use seq command in bash loops
Another practical use of the seq command is in for loops.
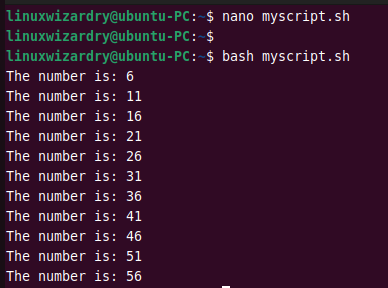
Create a new file myscript.sh and add the below content in it.
#!/bin/bash for num in $(seq 6 5 60) do echo "The number is: $num" done
You can run the above script using the bash command. It will iterate over the given sequence and print the following results.
bash myscript.sh
Output:
Conclusion
Now you know different ways of using the seq command to generate the sequence of numbers in Linux systems. The seq command offers limited functionality, but it comes in handy when used with other commands.
We hope this article helps you understand how to use seq command and print the list of sequence numbers quickly. If you have any questions or feedback, please let us know in the comment section.
